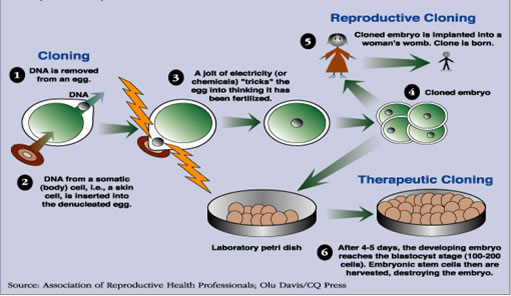
During the first step of cloning, the nucleus is removed from the female egg; this process, also known as somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), removes most of the genetic material of the egg and produces a enucleated egg. Then, the nucleus of a somatic cell is removed and put into the enucleated egg. The egg is then forced to divide, either through electricity or chemicals. For reproductive cloning, the embryo is then transplanted into a woman’s womb, whereas in therapeutic cloning, it is developed in a lab until the embryonic stem cells can be procured.
Click on the image below to watch a video on cloning.
Photo courtesy of Association of Reproductive Health Professionals